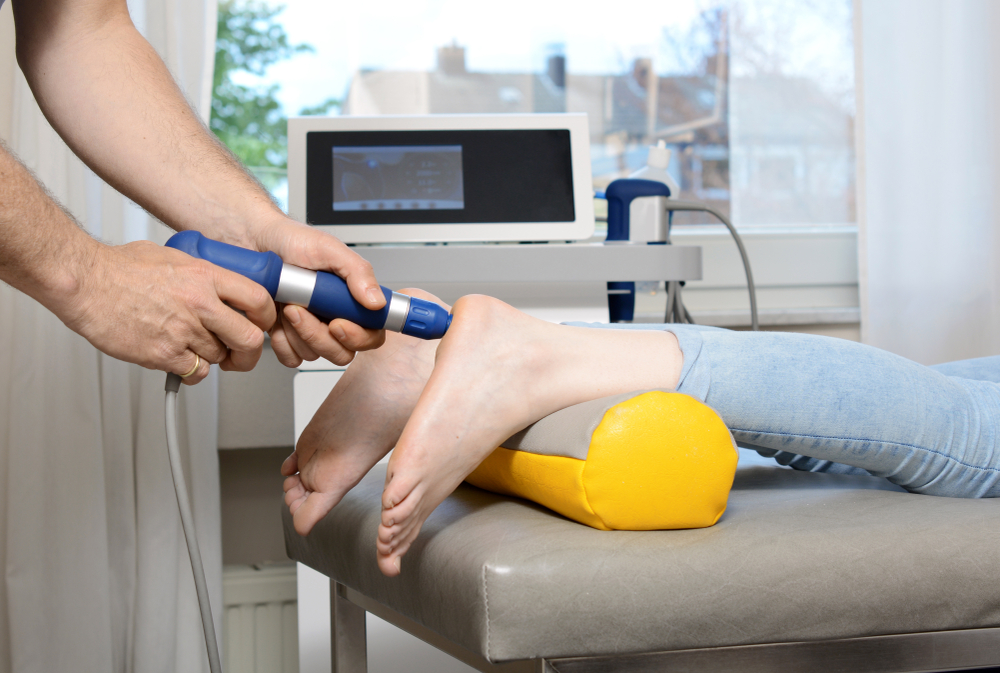
Shockwave Therapy
Introduction to Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive treatment technique that utilizes acoustic waves to stimulate healing in musculoskeletal tissues. It is commonly used to address various conditions involving tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues. The therapy involves the application of acoustic waves through a coupling medium, such as gel, which is transmitted to the affected area. These waves help to promote healing and alleviate pain.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy
Traction therapy works by manually or mechanically stretching the spine, which helps to:
- Reduce Pressure on Discs: By stretching the spine, traction decreases the pressure on the vertebral discs that may be causing pain.
- Enhance Disc Hydration: The decompression helps the discs to rehydrate and regain their natural shape and function.
- Alleviate Nerve Compression: Reducing disc pressure helps to relieve the compression on nearby nerves, thereby reducing pain and improving function.
Benefits of Shockwave Therapy
Pain Relief
- Mechanism: Shockwave therapy can reduce pain by interrupting the pain signal pathways and stimulating the body’s natural pain-relief mechanisms.
- Effect: Patients often experience significant pain reduction after a few sessions.
Enhanced Tissue Healing
- Mechanism: Acoustic waves stimulate cellular repair processes, promote blood flow, and increase the metabolism of the affected tissues.
- Effect: Accelerates the healing of injured tissues, including tendons and ligaments.
Improved Mobility and Function
- Mechanism: By reducing pain and promoting tissue healing, shockwave therapy can enhance joint and muscle function.
- Effect: Increases range of motion and overall functional abilities.
Reduction of Inflammation
- Mechanism: Shockwaves can help reduce inflammation in the affected area by increasing circulation and encouraging the removal of inflammatory substances.
- Effect: Decreases swelling and promotes faster recovery.
Breakdown of Calcifications
- Mechanism: Shockwave therapy can help break down calcified deposits in tendons and other tissues.
- Effect: Facilitates the removal of calcifications and improves the function of the affected area.
Promotion of Collagen Production
- Mechanism: The therapy stimulates fibroblasts, which are cells responsible for collagen production.
- Effect: Enhances the repair and regeneration of connective tissues, improving strength and elasticity.
Non-Invasive and Safe
- Mechanism: Shockwave therapy is a non-surgical treatment that does not require any incisions or invasive procedures.
- Effect: Reduces the risks associated with invasive treatments and has a favorable safety profile.
Quick Treatment Sessions
- Mechanism: Each treatment session is relatively short, typically lasting between 5 to 15 minutes.
- Effect: Allows for efficient management of time and integration into regular treatment schedules.
No Need for Anesthesia
- Mechanism: The procedure is performed without the need for anesthesia, as it is minimally uncomfortable.
- Effect: Patients can resume normal activities shortly after the session.
Common Uses of Shockwave Therapy
- Tendinitis and Tendinopathy: Treatment for conditions like Achilles tendinitis, rotator cuff tendinitis, and plantar fasciitis.
- Bursitis: Helps reduce inflammation in the bursae (fluid-filled sacs) around joints.
- Muscle Strains: Accelerates healing of strained muscles.
- Ligament Injuries: Supports recovery from sprains and tears in ligaments.
- Chronic Pain Conditions: Provides relief for chronic pain syndromes related to musculoskeletal disorders.
Shockwave therapy is often used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include physical therapy, exercise, and other modalities. It is important for patients to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of shockwave therapy for their specific condition and to tailor the treatment to their individual needs.